This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
Graphical Abstract
SUMMARY:
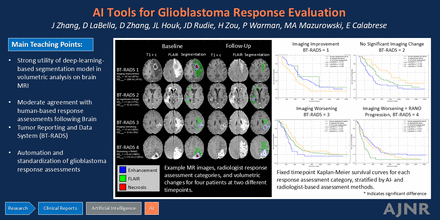
This project aimed to develop and evaluate an automated, AI-based, volumetric brain tumor MRI response assessment algorithm on a large cohort of patients treated at a high-volume brain tumor center. We retrospectively analyzed data from 634 patients treated for glioblastoma at a single brain tumor center over a 5-year period (2017–2021). The mean age was 56 ± 13 years. 372/634 (59%) patients were male, and 262/634 (41%) patients were female. Study data consisted of 3,403 brain MRI exams and corresponding standardized, radiologist-based brain tumor response assessments (BT-RADS). An artificial intelligence (AI)-based brain tumor response assessment (AI-VTRA) algorithm was developed using automated, volumetric tumor segmentation. AI-VTRA results were evaluated for agreement with radiologist-based response assessments and ability to stratify patients by overall survival. Metrics were computed to assess the agreement using BT-RADS as the ground-truth, fixed-time point survival analysis was conducted to evaluate the survival stratification, and associated P-values were calculated. For all BT-RADS categories, AI-VTRA showed moderate agreement with radiologist response assessments (F1 = 0.587–0.755). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis revealed statistically worse overall fixed time point survival for patients assessed as image worsening equivalent to RANO progression by human alone compared to by AI alone (log-rank P = .007). Cox proportional hazard model analysis showed a disadvantage to AI-based assessments for overall survival prediction (P = .012). In summary, our proposed AI-VTRA, following BT-RADS criteria, yielded moderate agreement for replicating human response assessments and slightly worse stratification by overall survival.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- 2D
- 2-dimensional
- AI
- artificial intelligence
- AI-VTRA
- artificial intelligence volumetric tumor response assessment
- BT-RADS
- Brain Tumor Reporting and Data System
- C-index
- concordance index
- FeTS
- Federated Tumor Segmentation
- GBM
- glioblastoma
- IDH
- isocitrate dehydrogenase
- NLP
- natural language processing
- OS
- overall survival
- RANO
- Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology
- RECIST
- Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors
- SD
- standard deviation
- VDET
- volumetric differences for enhancing tumor
- VDFLAIR
- volumetric differences for FLAIR
- © 2025 by American Journal of Neuroradiology