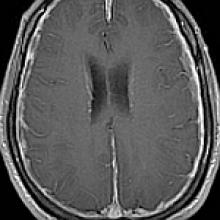
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Syndrome in which low CSF volume results in orthostatic headache
- Generally due to CSF leakage through a dural defect
- May be related to predisposing underlying structural weakness of the spinal meninges
- Key Imaging Features: related to Monro-Kellie hypothesis: loss of CSF from subarachnoid space → increase in total intracranial blood volume causing enlargement of dural venous sinuses, epidural vertebral venous plexus, and pituitary gland. Transudation of intravascular fluid into subdural space causes dural enhancement and subdural fluid collections. Mass effect from subdural collections and decreased surrounding CSF cause brain sagging.
- CT or MR myelography useful to find source of CSF leak
- Treatment: Epidural blood patch