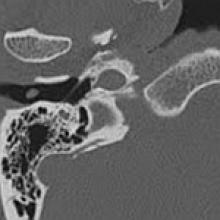
Persistent Stapedial Artery (PSA)
- The stapedial artery is transiently present in normal fetal development and connects the future external carotid artery to the internal carotid artery. If it does not regress, a PSA can be seen on otoscopic and CT examinations.
- A PSA is a rare vascular anomaly. It can occur in association with an aberrant carotid artery.
- It can cause conductive hearing loss or tinnitus; most patients are asymptomatic.
- Imaging identification of this variant is necessary to obviate unnecessary surgery, and may help in planning surgical or endovascular interventions.
- Key Diagnostic Features: Absence of foramen spinosum and presence of a soft-tissue linear structure leaving the carotid canal crossing the middle ear over the promontory, sometimes causing the pseudo-appearance of duplicated facial nerve canal is suggestive of PSA. Diagnosis can be established on HRCT temporal bone, CT/MR angiography, and conventional angiography.
- DDx: glomus tympanicum, aberrant carotid artery
- Rx: If symptomatic, surgical ligation or endovascular occlusion may be considered.