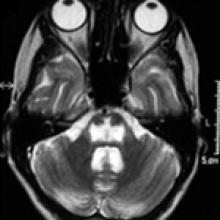
Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome
- Rapid correction of chronic osmolar imbalance, especially in the presence of concurrent malnutrition, can cause rapid demyelination. This can also occur with normal serum sodium.
- This has classically been described as affecting the central pons (central pontine myelinolysis). However, it also commonly affects other white matter areas (extra pontine myelinolysis) and causes demyelination typically in the basal ganglia, corpus callosum and cerebral white matter.
- Patients can present with an altered mental state, bradypnea, spastic paraparesis and even a "locked in" syndrome.
- Treatment is supportive, with survivors likely to require an extended period of neurorehabilitation.